Why Are Home Insurance Rates Sky High In The USA?
Why Are Home Insurance Rates Sky High In The USA?
In recent years, homeowners across the United States have been facing a significant and often unexpected financial burden: skyrocketing home insurance rates. For many, this has come as a surprise, especially when combined with the rising costs of homeownership in general. But what’s behind these escalating rates? Let’s dive into the key factors driving up home insurance premiums.

1. Increased Frequency and Severity of Natural Disasters
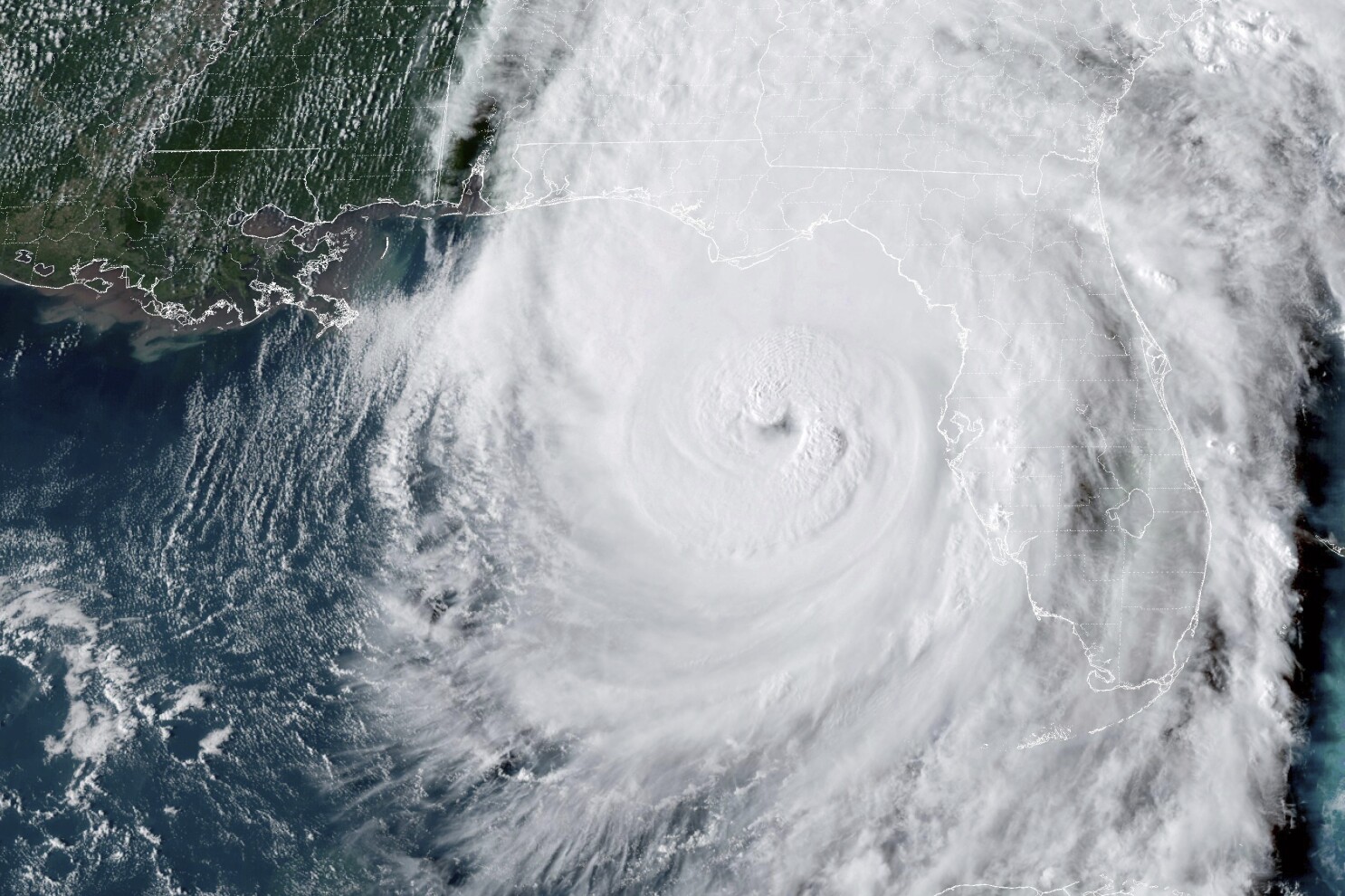
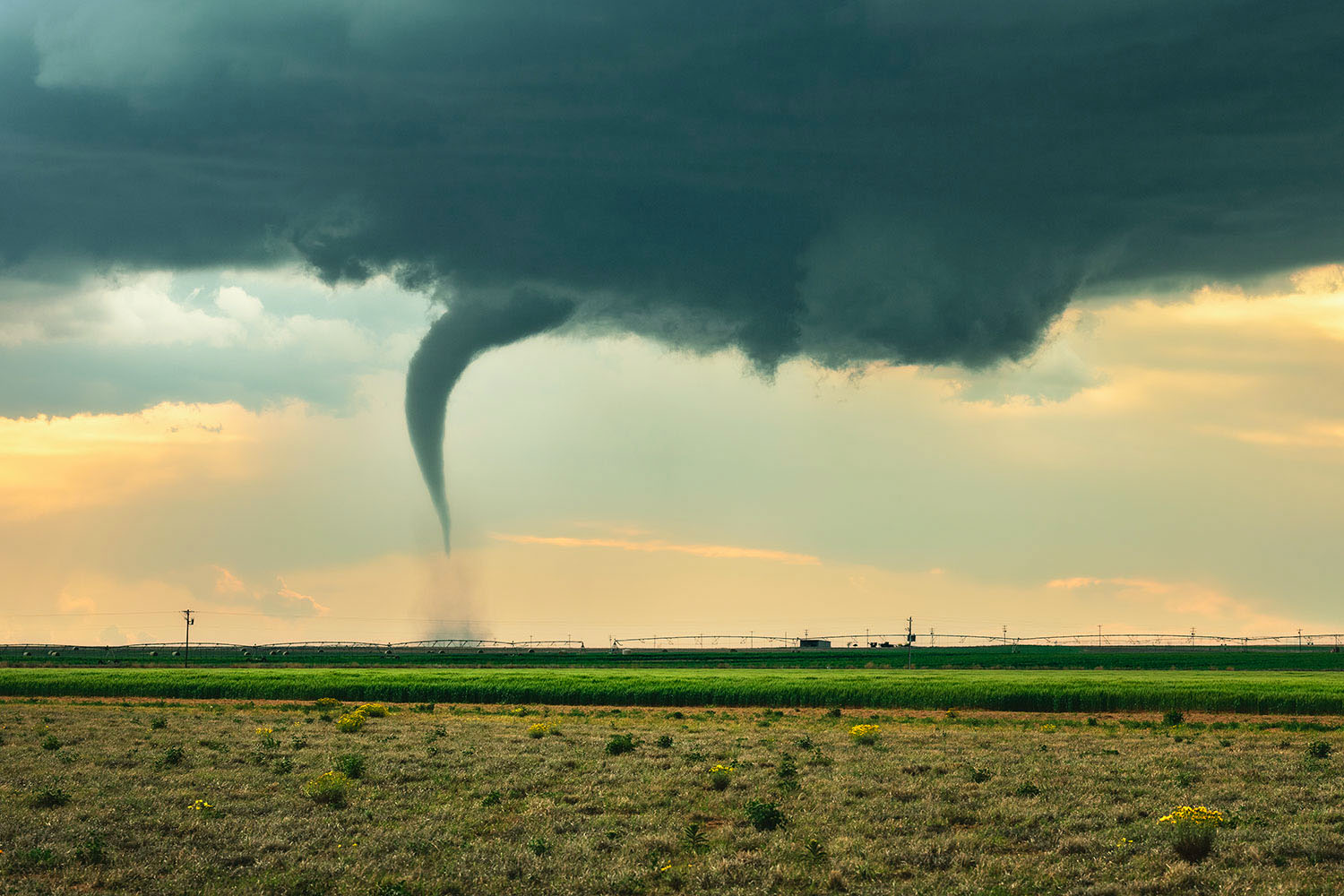
One of the most significant contributors to rising home insurance rates is the increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters. Events such as hurricanes, wildfires, floods, and tornadoes have become more common, and their impacts are more devastating than ever. Insurance companies are paying out more in claims, which drives up the cost of premiums for everyone. In regions particularly prone to these events, such as coastal areas vulnerable to hurricanes or drought-prone states susceptible to wildfires, the increase in rates can be especially pronounced.
2. Climate Change and Its Impact
Closely tied to natural disasters is the broader issue of climate change. As global temperatures rise, so does the risk of extreme weather events. Warmer oceans fuel stronger hurricanes, while prolonged droughts increase the likelihood of wildfires. Insurance companies must adjust their models to account for these heightened risks, which leads to higher premiums. Additionally, properties that were once considered safe from certain types of disasters may now be at risk, further complicating the insurance landscape.

3. Rising Costs of Construction and Repairs
Another factor contributing to higher home insurance rates is the rising cost of construction materials and labor. Supply chain disruptions, inflation, and increased demand have all pushed up the price of materials such as lumber, steel, and concrete. When homes are damaged or destroyed, the cost to rebuild or repair them is significantly higher than it was just a few years ago. Insurance companies must factor these increased costs into their pricing models, resulting in higher premiums for homeowners.
4. Aging Infrastructure and Homes
Many homes and infrastructures in the U.S. are aging. Older homes are more prone to issues such as plumbing leaks, electrical problems, and structural damage, all of which can lead to costly insurance claims. As these homes continue to age, the likelihood of an insurance claim increases, which in turn drives up the cost of premiums. Additionally, older homes may not be up to current building codes, which can make them more vulnerable to damage during a disaster, further increasing insurance risks.

5. Reinsurance Costs and Global Market Pressures
Insurance companies don’t shoulder all the risk themselves; they rely on reinsurance companies to help manage the potential for large-scale claims. However, reinsurance costs have been rising, influenced by global factors such as natural disasters in other parts of the world and financial market volatility. These increased costs are passed down to consumers in the form of higher premiums.

6. Increased Litigation and Fraud
The insurance industry has also seen a rise in litigation and fraudulent claims, both of which can drive up costs. In some areas, homeowners are more likely to file lawsuits against insurance companies, or there may be higher instances of fraudulent claims being made. To offset these risks, insurance companies may increase premiums to cover the potential costs of legal battles and payouts for fraudulent claims.

7. Insurance Companies Adapting to New Risks
As the world changes, so do the risks that insurance companies must cover. The rise of cyber threats, for example, has added a new layer of risk for homeowners, as more people work from home and use smart devices. Additionally, the increased use of home-sharing services like Airbnb introduces new liabilities that insurance companies must consider. As insurers adapt to these evolving risks, they may adjust their pricing models, resulting in higher premiums.

What Can Homeowners Do?
While it may seem like there’s little homeowners can do to combat rising insurance rates, there are steps that can be taken to mitigate costs:
- Shop Around: Different insurance companies assess risks differently, so it pays to get multiple quotes.
- Bundle Policies: Many insurers offer discounts for bundling home insurance with other types of coverage, such as auto insurance.
- Invest in Home Improvements: Upgrading your home’s systems (e.g., plumbing, electrical) or adding protective features (e.g., storm shutters, security systems) can reduce your risk and potentially lower your premiums.
- Increase Your Deductible: A higher deductible means lower premiums, but be sure it’s an amount you can afford to pay out-of-pocket if needed.

The rise in home insurance rates is a complex issue influenced by a multitude of factors, from climate change and natural disasters to the rising costs of construction and global market pressures. While these increases are challenging for homeowners, understanding the reasons behind them can help you make informed decisions and potentially find ways to reduce your insurance costs. As we navigate this new landscape, it’s important to stay informed and proactive in managing our financial risks.









